Should you have Radon Testing done?
Radon Facts:
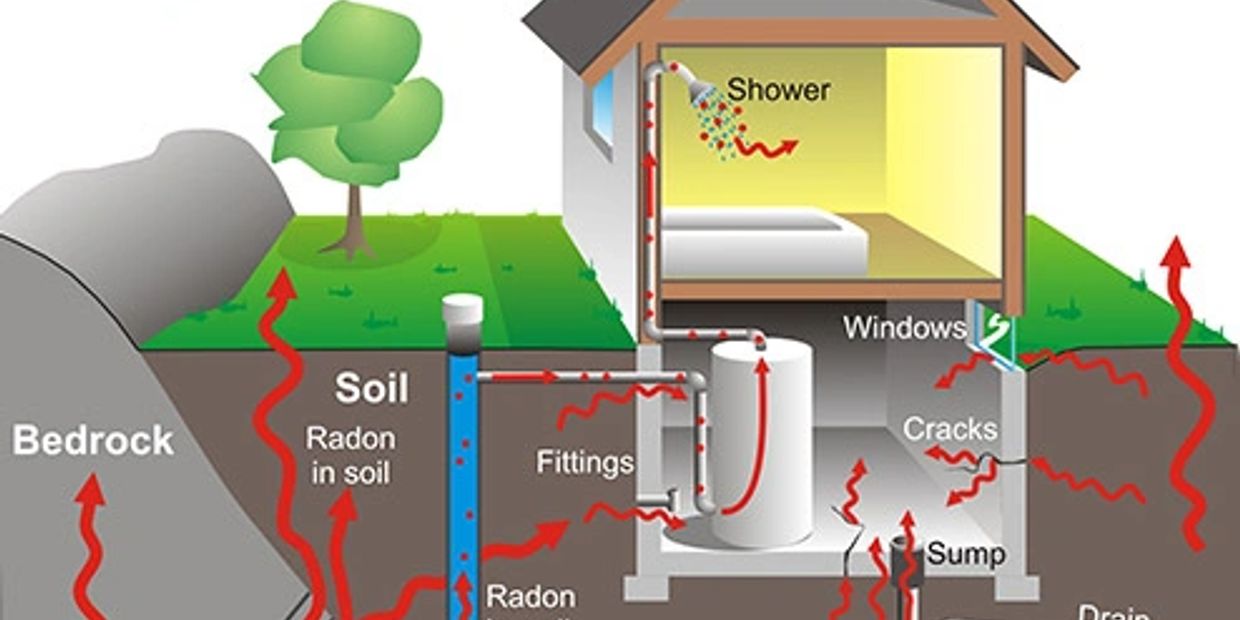
Breathing radon in your home can cause lung cancer. Radon is a naturally occurring radioactive gas released in rock, soil, and water that can build up to dangerous levels inside any home, including both new and old homes, well-sealed and drafty homes, as well as homes with or without a basement. This odorless and invisible gas means the only way to know if your home has a radon problem is to test for it. Conducting a home inspection in Rockland County can help identify radon levels in your property. Breathing radon can increase your risk of lung cancer, making it a significant concern. In fact, radon is the number one cause of lung cancer among non-smokers and the second leading cause for smokers. The EPA estimates that radon causes more than 20,000 deaths from lung cancer each year in the U.S. If you smoke and your home has a high radon level, your risk of lung cancer can increase even more. Radon has been found in every state, and homes with high levels have been detected throughout the country, including in Rockland County NY. Radon levels can vary greatly from home to home; even homes next door can have very different levels. Radon is measured in picocuries per liter of air (pCi/L), indicating radioactivity. In the United States, the average indoor radon level is about 1.3 pCi/L, while the average outdoor level is around 0.4 pCi/L. The U.S. Surgeon General and EPA recommend fixing homes with radon levels at or above 4 pCi/L. They also suggest that homeowners consider remediation for radon levels between 2 pCi/L and 4 pCi/L. You should test for radon, and engaging with home inspectors in Rockland County NY can facilitate this process. Testing your house for radon is straightforward, and if a radon problem is detected, it can be fixed. Addressing a radon problem reduces the risk of lung cancer for you and your family. A simple test will reveal if your home has a high radon level.
The best way to decide whether or not to test for Radon is to educate yourself and make an informed decision